“Militaries and intelligence bodies do not necessarily want to steal or manipulate data; they want to influence information and change opinions and perceptions”, Alexander Klimburg
One of the prevailing challenges, in the region these coming days, is the rising threats in cybersecurity (it is spelled in one word because it is treated entirely like a unique newly coined word, not just a combination of two words or implying another form of security, like maritime security).
To prove my point, securing the cyber (another way of expressing the term not as a single word) definitely refers to the prevention of data breach, stealing and falling of sensitive data into the wrong hands. It is about safeguarding the network structures not to be infiltrated or disabled.
In the point of view of the Department of National Defense (DND), cybersecurity is beyond data breach. It includes: cyber recruitment of radicals, cyber espionage, cybercrimes, hacktivism and cyber terrorism that may involve damage to properties and loss of lives e.g. through tinkling of: electrical gridlines, air traffic control, drinking water, streetlights, sanitation systems, 911 dispatch, stock markets, hospitals, Global Positioning System (GPS), Heat Ventilations and Air Condition (HVAC) Systems and other Internet of Things (IOTs). So for DND, it is about addressing cyber operations made by the enemies-of-the-state.
The primary mandate of DND is, “to maximize its effectiveness and efficiency for guarding against internal and external threats to national peace”.
So in this manner, DND has declared and now recognizes Cyberspace as the new dimension in warfare. Its new role is Cyber Defense, which covers and encompasses cybersecurity. In its Strategic Plan, the cyber component, C4ISTAR, will be the key factor for our success in battle at land, sea and air (Network Centric).
However, cybersecurity, as a newly coined word, still has so many meanings and no definite definition yet. When I sat as co-chair of New Zealand in the ASEAN Defense Ministers’ Meeting (ADMM)-Plus Experts’ Working Group (EWG) for Cybersecurity, I gave cybersecurity a new definition, “It is not simply reacting to threats but it is about shaping creative and sustainable combinations of technological and social responses at an international level. With such set-up, we can build better confidence, better transparency, better cooperation and ultimately better stability in the ASEAN Region”.
I know there will be more interpretations coming out. Until now, New Zealand, for instance, has no legal definition for cybersecurity in their NZDF (New Zealand Defense Force) primer on cybersecurity. The primer nevertheless discussed cyber capability and cyber operations.
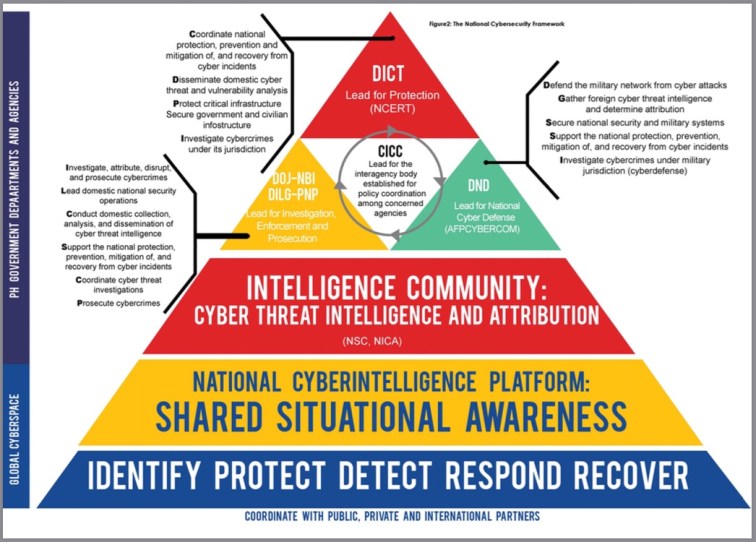
DICT, in their National Cybersecurity Master Plan 2022 manual, has designated DND as the lead agency for National Cyber Defense, to be implemented by a unit called – AFPCYBERCOM. DICT even went farther by enumerating, in the said manual, the roles and responsibilities of DND, which are:
1) Defend the military networks from cyber attacks;
2) Gather foreign cyber threats intelligence and determine attribution;
3) Secure national security and military systems;
4) Support the national protection, prevention, mitigation of, and recovery from cyber incidents; and
5) Investigate cybercrimes under military jurisdictions.
Honestly, DICT never consulted DND! Likewise, there is still no AFPCYBERCOM yet. The first draft of DICT master plan even said that the primary task of DND is “to defend the country from cyber-attack” I was caught off guard! What an ambitious marching order for DND? The blame will fall everything on my shoulders.
Anyway, let me explain in a way you won’t lose faith with DND for unpreparedness but heighten your level of confidence for over preparation, what is going in the defense department regarding cybersecurity? Even without DICT saying the tasks in their master plan, J6 has been covering tasks #1, #3 and #4 all along; on the other hand, J2 is taking full control of tasks #2 and #5 ever since. These two (2) J-Staffs are well supported and always keep the Department informed and updated.
Moreover, DND is in the process of developing well its 5 focused areas (based from the Global Cybersecurity Indexing): 1) Legal, 2) Technical, 3) Organizational, 4) Capability-Building, and 5) Cooperation. These are self-explanatory.
For instance, DND has transformed the Defense Situation Monitoring Center (DSMC) into a world-class Cyber Center where the ASEAN Direct-Communication Infrastructure (ADI), a telephone hot-line amongst Defense Ministers, is housed. DSMC is connected with all cyber centers or point-of-contacts of ADMM+ member-states for information sharing on cyber matters. In connection with this, a cellphone apps “Alerto” (both in ios and android) will be launched this year as an apparatus for everybody in reporting cyber incidents to DSMC. DND needs your help on this and please be counted!
On the 27th of February this year, in cooperation with the Department of Foreign Affairs (DFA), DND will be hosting a symposium entitled, “DarkNet: the New Soceital, Legal, Technological and Ethical Challenges” It will be about recruitment of ISIS radicals through the internet and how to catch and prevent them.
I have been mentioning “cyber” since the start of this article and I hope you already have an idea what cyber is? It is anything relating to computers, computerized machines or smart gadgets controlled by programs or remote controls running through networks of networks, to include the internet.
When we come to the words security and defense, many IT practitioners in the industry still do not know the difference. They usually interchange the use of these words. They use the word defense even they are just referring to security, which is only a part of defense.
My cellphone dictionary defines security as the state of being safe; freedom from the occurrence or risk of injury, danger or loss. In my own perception, it is all about building up and establishing a sense of confidence that guarantees everything will go smoothly running. There is a promise of assurance that no mistakes, harm or danger that could happen. Security is proactive; while defense is reactive. It is only in defense, where clashes among protagonists may happen. Security is purely a psychological issue. It is just a pursuit of a feeling, a feeling of being safe and secure.
To establish this feeling of security in IT, we carry out hygiene and hardening tasks.
Cyber hygiene is similar to our personal hygiene. The metaphor is used to tell us also to keep our computers clean and healthy. We should use reputable anti-virus software in scanning our drives, be conscious of using contaminated external drives, clicking unknown files and images in your emails and internet and more.
In hardening, Wikipedia describes it well: “In computing, hardening is usually the process of securing a system by reducing its surface of vulnerability, these activities are: keeping security patches updated; installing firewall; closing certain ports; not allowing file sharing among programs; installing virus and spyware protection; creating strong passwords; keeping backups; disabling cookies; and using encryption when possible”.
In Defense, there must be a blocking force or counteraction. Defense is much bigger in scope compared to security. The word “defense” usually goes along with the word “offense”. These are the two sides of the coin. May it be in sports or combat. My cellphone dictionary defines defense as a resistance to attack; a fortification; stopping someone from doing something by defeat; and a capacity to react. The definition of defense must contain all of these elements, where fortification is part of it. I therefore conclude the definition of defense can be shown in this formula:
DEFENSE = SECURITY + COUNTERATTACK
When the terminology “cybersecurity” refers to cyberwarfare, this must be the concern of DND and the right term is Cyber Defense. If cybersecurity is talking about computer hygiene and hardening, the term is in two words – “cyber security” and this must be the concern of DICT. For the one-word “cybersecurity” by itself, you may still continue to create your own definition . . .
I also keep on repeating in my lectures: in any warfare, may it be in land, sea, air and now cyber, we have to identify first our own forces before engaging in a fight. In land, it is the Army; in sea, it is the Navy; in the air, it is the Air Force; and in cyber, we have the Signal Corps. DND has all these forces and it is prepared to defend the country anytime anywhere, may it be in land, sea, air and even in CYBERSPACE. All ready to fight and win!
Disclaimer:
This article was written in my personal capacity. The opinions expressed here are my own and do not reflect the view of the Department of National Defense (DND).
